How Stator Assemblies Power Motor Systems

The stator assembly is the heart of an electric motor, generating a rotating magnetic field the stator assembly. The stator assembly allows the motor to transform the electrical energy into mechanical energy, which used in devices from household appliances to electric vehicles. Let’s dive into the wonders of the stator assembly from a science perspective, exploring its functions, applications, secrets to efficiency improvement, and manufacturing process.
- Stator Core: Made of thin, stacked silicon steel sheets, resembling neatly layered metal slices, it forms a pathway for the magnetic field while minimizing energy loss.
- Copper Windings: Insulated copper wires wound around the core, which generate a magnetic field when electrified, acting as the “magnetic field generator.”
- Lead Wires: Connect the windings to an external power source, ensuring smooth current transmission.
- Insulation Materials: Encase the windings and core to prevent leakage or short circuits, serving as a “protective shield” for the circuit.
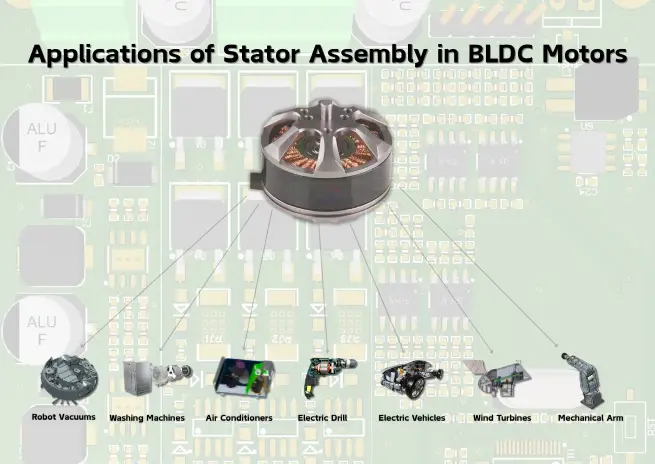
Applications of Stator Assembly in BLDC Motors
- Robot Vacuums: The stator powers compact motors, enabling the robot to maneuver and clean flexibly.
- Washing Machines: The stator ensures the drum rotates efficiently, saving energy.
- Air Conditioners and Refrigerators: The stator drives the compressor (a component that compresses refrigerant), achieving efficient cooling.
- Power Tools: In tools like electric drills, the stator provides robust power.
- Electric Vehicles: The stator drives the motor, powering eco-friendly transportation.
- Wind Turbines: The stator converts wind energy into electrical energy, supporting clean energy production.
- Robotics: The stator powers robotic arms, enabling precise operations.
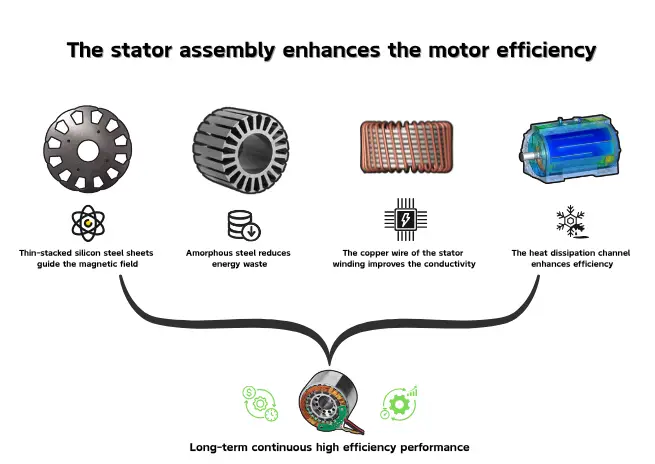
How the Stator Assembly Improves Motor Efficiency
The design and materials of the stator assembly directly determine a motor’s efficiency. An efficient stator generating maximum power with minimal electrical energy. Here are the secrets behind how the stator boosts efficiency:
First, The stator core is composed of thin, stacked silicon steel sheets that resemble layered metal slices. These sheets form a magnetic circuit, guiding the magnetic field efficiently. The laminated structure reduces eddy currents and hysteresis loss, allowing electrical energy to focus on driving the rotor. Modern motors even use amorphous steel, a low-loss material, to further minimize energy waste.
Second, the stator windings, made of insulated copper or aluminum wires, generate a rotating magnetic field to drive the rotor. Copper or aluminum wire, used as stator windings, can create movement. The copper wires, owing to their greater conductivity, allow us to do away with copper loss. the winding of machine equipment without slots that are to be found in brushless DC motors can reach an efficiency of even 96%.
Additionally, thermal management is crucial. The stator generates heat during operation, and overheating reduces efficiency. Modern motors incorporate heat dissipation channels in the motor frame or even use liquid cooling to “cool down” the stator, ensuring sustained high-efficiency performance over time.
Manufacturing the Stator Assembly
Manufacturing a stator assembly is like crafting a precision instrument, with every step being critical. In particular, the stator for flat-wire motors is known for its efficiency and compactness. Below is the stator manufacturing process to take you inside the production workshop.
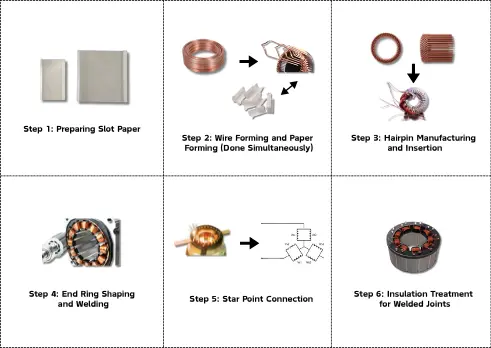
Step 1: Preparing Slot Paper
Stator manufacturing begins with slot paper, an insulating material that acts like a “protective coat” for the core slots, preventing electrical leakage from the windings. Workers use machines to cut the insulating paper into precise shapes and insert it into the slots of the stator core, like laying an “insulating foundation” for the magnetic pathway.
Step 2: Wire Forming and Paper Forming (Done Simultaneously)
Alongside slot paper preparation, wire forming and paper forming take place. Wire forming involves shaping flat copper wires into a “hairpin” shape, like bending metal wire into U-shaped clips for easy insertion into the core. Paper forming adjusts the insulating paper’s shape to fit snugly with the hairpin coils.
Step 3: Hairpin Manufacturing and Insertion
Precision machines bend copper wires into hairpin shapes, with each hairpin identical in size, like crafting a row of uniform “magnetic field components.” Then comes hairpin insertion, where workers or machines insert the hairpin coils into the core slots, ensuring the coils are neatly arranged.
Step 4: End Ring Shaping and Welding
Once the hairpins are inserted, the next step is to join their ends so that a complete circuit is formed. While the end ring shaping operation changes the form of the ring to match the hairpin ends, the end ring welding operation uses high heat to join the ring and hairpins together.
Step 5: Star Point Connection
The star point is the motor circuit’s connection hub, linking the hairpin coils into a cohesive whole, ensuring even magnetic field distribution to drive the rotor efficiently.
Step 6: Insulation Treatment for Welded Joints
Welds subjected to weathering are a very high possibility of moisture developing attraction leading to short circuits, they are covered with insulating varnish or enveloped by insulating material just like when you put a waterproof jacket on them. This measure also leads to the long lifetime of the stator and the sturdiness of the motor.
All the stages of the manufacturing process together make it look as though we are assembling a small scale “energy converter,” each successive stage being the basis for efficiency and reliability. Finally, these stators find application in electric cars, washing machines, and wind turbines, resulting in green energy and the reduction of energy waste.

I'm dedicated to popular science writing about magnets. My articles mainly focus on their principles, applications, and industry anecdotes. Our goal is to provide readers with valuable information, helping everyone better understand the charm and significance of magnets. At the same time, we're eager to hear your opinions on magnet-related needs. Feel free to follow and engage with us as we explore the endless possibilities of magnets together!



